Submerged under the sea for over a thousand years, two lost cities of ancient Egypt were recently rediscovered. Their story is told for the first time in what is expected to be a blockbuster exhibition at the British Museum – Sunken Cities: Egypt’s Lost Worlds.
Vanished beneath the waters of the Mediterranean, the lost cities of Thonis-Heracleion and Canopus lay at the mouth of the Nile. Named after the Greek hero Heracles, Thonis-Heracleion was one of Egypt’s most important commercial centres for trade with the Mediterranean world and, with Canopus, was a major centre for the worship of the Egyptian gods. Their amazing discovery is transforming our understanding of the deep connections between the great ancient civilisations of Egypt and Greece. The Sunken Cities: Egypt’s Lost Worlds exhibition at the British Museum is on 19 May-27 November 2016.
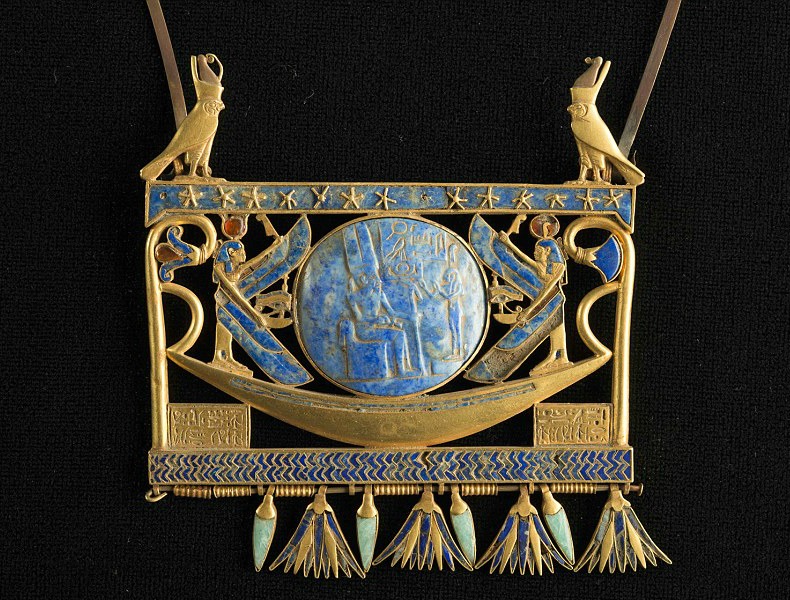 Pectoral in gold, lapis lazuli and glass paste, found in Tanis in the royal tomb of the Pharaoh Sheshonk II (~ 890 BC), Egyptian Museum, Cairo. Photo Credit: ©Christoph Gerig via Franck Goddio/Hilti Foundation.
Pectoral in gold, lapis lazuli and glass paste, found in Tanis in the royal tomb of the Pharaoh Sheshonk II (~ 890 BC), Egyptian Museum, Cairo. Photo Credit: ©Christoph Gerig via Franck Goddio/Hilti Foundation.






Leave a Reply