London has won two prestigious accolades at the annual Condé Nast Traveller Readers’ Choice Awards 2016. The capital came out on top as Best United Kingdom City for the 6th year running, and Best United Kingdom City for Restaurants and Bars for the second consecutive year in the reader-nominated awards ceremony at Soho’s Ham Yard Hotel recently.
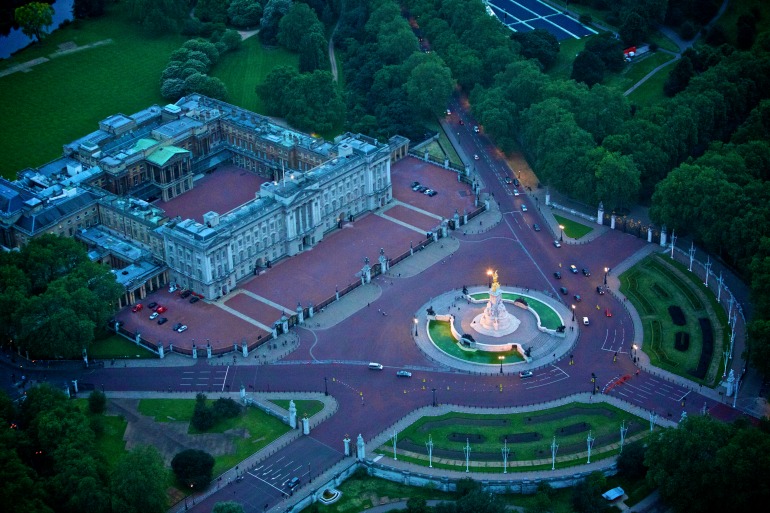 Buckingham Palace: Aerial shot at night. Photo Credit: ©London & Partners.
Buckingham Palace: Aerial shot at night. Photo Credit: ©London & Partners.
The awards from the readers of one of the most popular travel magazines in the world comes as recent research from London & Partners, the Mayor’s official tourism body for London found that last year, overseas visitors made 18.7 million visits to the city’s best known cultural institutions, which is 1.8 million more than in 2012.
Separate research also reveals that London’s booming tourism trade is set to continue post-Brexit, as two thirds of Americans who visited in the last two years said they will definitely return due to a more favourable exchange rate.
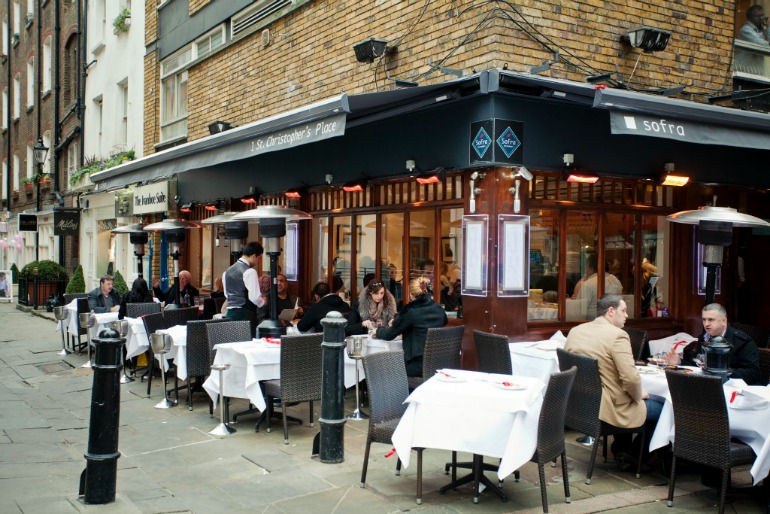 London West End, Marylebone St, Christopher’s Place restaurant. Photo Credit: ©London & Partners.
London West End, Marylebone St, Christopher’s Place restaurant. Photo Credit: ©London & Partners.






Leave a Reply